Introduction: Understanding Market Research Methods
In today’s competitive, data-driven world, knowing your customers isn’t optional; it’s essential. That’s where market research methods come in.
Whether you’re a startup testing a new product idea or a global brand refining its strategy, market research helps you uncover what people truly want, how they behave, and why they make purchasing decisions.
Simply put, market research methods are the techniques businesses use to collect, analyze, and interpret data about their target market. These methods reveal valuable insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitors helping organizations make informed, low-risk decisions.
Quick Definition :
Market research methods are structured techniques used by businesses to collect and analyze data about customers, markets, and competitors. Common methods include surveys, focus groups, interviews, observation, and data analytics.
What Are Market Research Methods?
Market research methods are the structured techniques used to collect, analyze, and interpret data about markets, products, and customers. They help transform raw information into actionable business insights.
Every company — from tech startups to established brands — uses different research methods depending on its goals, budget, and timeline. For example:
- A startup might use online surveys to validate product ideas.
- A marketing team might use focus groups to test a new ad campaign.
- A retail chain might analyze customer purchase data to improve store layout.
Purpose of Market Research Methods
These methods help answer specific questions, such as:
- How large is the target market?
- What are the latest consumer trends?
- What drives customer satisfaction?
- How effective are our current marketing efforts?
Types of Market Research Methods (Overview)
Before diving into the tools and techniques, it’s important to understand the two main categories of market research:
- Primary Research – Collecting new, first-hand data directly from the source.
- Secondary Research – Using existing data from reliable, published sources.
Additionally, each can be either qualitative (understanding opinions and emotions) or quantitative (measuring facts and statistics).
| Type | Data Source | Focus | Examples |
| Primary Research | First-hand | Custom insights | Surveys, Interviews, Focus Groups |
| Secondary Research | Existing data | Broader context | Reports, Databases, Market Studies |
| Qualitative | Subjective | Why people act | Focus Groups, Interviews |
| Quantitative | Objective | What people do | Surveys, Analytics |
These methods often work best when combined — for instance, using quantitative data to spot trends and qualitative insights to understand why they occur.
Primary Market Research Methods
Definition & Purpose
Primary research involves collecting original data directly from your audience. It’s ideal when you need current, specific insights that existing data can’t provide.
This method helps businesses:
- Validate product ideas before launch
- Understand evolving customer needs
- Measure brand perception and satisfaction
Examples of Primary Research Methods
- Surveys & Questionnaires
Surveys are one of the most popular research tools. They use structured questions to gather opinions or feedback from a target audience.
Tools like Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, and Typeform make it easy to collect and analyze results quickly. - Focus Groups
A focus group brings together a small group of people to discuss their perceptions and experiences about a product or idea. It helps uncover emotional and behavioral insights that numbers alone can’t reveal. - Interviews
In-depth, one-on-one interviews provide detailed qualitative insights. They’re especially useful for complex topics like brand loyalty or consumer motivation. - Observation Studies
Instead of asking people what they do, observation studies watch how they behave in real life — such as how customers interact with products on a store shelf or navigate a website.
Pro Tip:
Always define your research goals before selecting a method. If you want fast, measurable feedback — use surveys. If you want deeper emotional understanding, use interviews or focus groups.
Secondary Market Research Methods
Definition & Scope
Secondary research (also known as desk research) involves analyzing data that has already been collected by others. It’s cost-effective and helps you gain a big-picture view of the market.
Common Data Sources
- Government Reports: Census data, labor statistics, or economic indicators.
- Industry Publications: Market reports from organizations like Nielsen or Statista.
- Academic Papers & Journals: Peer-reviewed insights on industry trends.
- Online Databases: Resources like Google Scholar, MarketResearch.com, or company annual reports.
Answer Box:
Secondary market research uses existing data from sources such as government agencies, trade associations, and research firms to evaluate market conditions, industry trends, and consumer behavior.
This approach is best for identifying opportunities, sizing up competitors, or understanding broad industry trends before diving deeper with primary research.
Qualitative Market Research Methods
Qualitative research explores why people think, feel, and behave in certain ways.
It’s more about depth than numbers, uncovering emotional triggers and motivations.
Popular Qualitative Methods
- Focus Groups: Capture opinions through discussion.
- In-Depth Interviews: Explore personal perspectives.
- Ethnographic Research: Observe users in their natural environment.
- Online Communities: Gather feedback from engaged user groups.
Example:
A skincare brand might conduct focus groups to test how customers perceive a new packaging design — not just what they think of it, but how it makes them feel.
Quantitative Market Research Methods
Quantitative research focuses on measurable data and statistical validation. It answers questions like how many, how often, or how satisfied customers are.
Common Quantitative Methods
- Online Surveys: Collect large sample sizes for numerical analysis.
- Experiments: Test variables (e.g., pricing, promotions).
- A/B Testing: Compare two versions of a website, ad, or product feature.
- Data Analytics: Use tools like Google Analytics or Tableau to analyze behavior.
Example:
An e-commerce company may test two homepage designs to determine which one leads to higher sales conversion — that’s A/B testing in action.
Online & Digital Market Research Methods
The digital revolution has transformed market research. Businesses now have access to real-time, large-scale data through online tools and social platforms.
Modern Digital Techniques
- Social Media Listening: Analyze brand mentions, trends, and sentiments.
- Web Analytics: Track website traffic and user interactions.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predict trends and personalize user experiences.
- Online Polls: Quick feedback loops for small decisions.
Example:
A fashion retailer can use Instagram polls and hashtag analysis to predict which colors or styles will trend next season.
List of Market Research Methods (Top 10 Explained)
There’s no single “best” market research method — the right one depends on your business goal, target audience, and budget.
Below are the 10 most effective market research methods, divided into primary and secondary categories, with clear explanations, advantages, and examples.
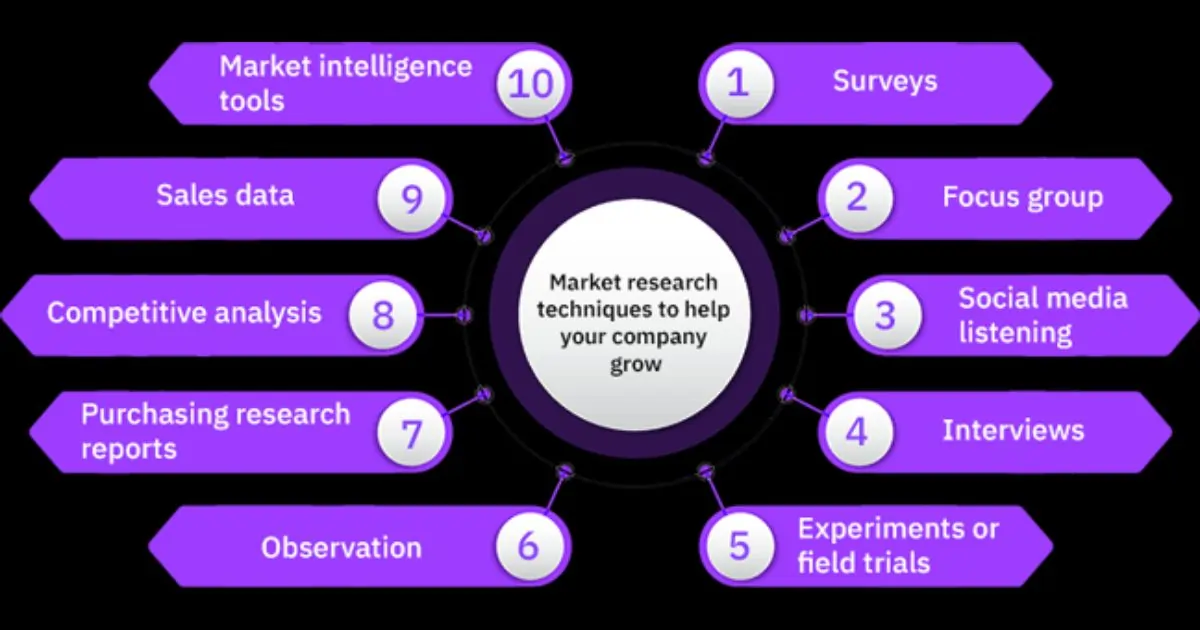
1. Surveys and Questionnaires (Primary Research)
What it is:
Surveys are one of the most popular ways to collect direct customer feedback. They use structured questions — multiple-choice, rating scales, or open-ended — to understand preferences, satisfaction, and buying behavior.
Example:
A coffee shop sends a short online survey asking customers about their favorite drink flavors and morning routines.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective and scalable
- Easy to analyze with tools like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey
- Provides quantitative insights (numbers and trends)
Disadvantages:
- Risk of low response rates
- Limited depth — answers may lack emotional context
2. Focus Groups (Primary Research)
What it is:
Focus groups bring together 6–10 participants to discuss a specific topic, product, or service guided by a moderator. It’s ideal for exploring opinions, emotions, and motivations.
Example:
A tech company gathers a focus group to test reactions to a new smartphone prototype before launch.
Advantages:
- Offers deep qualitative insights
- Uncovers emotional triggers and user preferences
Disadvantages:
- Expensive and time-consuming
- Risk of group bias (people may agree with others)
3. Interviews (Primary Research)
What it is:
One-on-one interviews (in-person or virtual) help you dive deep into customer experiences, perceptions, and challenges.
Example:
A software firm interviews business owners to learn how they manage customer data and what features they want in CRM tools.
Advantages:
- Detailed, personalized feedback
- Builds strong user empathy for product design
Disadvantages:
- Time-intensive
- Hard to generalize results from small samples
4. Observation (Primary Research)
What it is:
Observation means watching customers in real-life settings — online or offline — to see how they behave naturally.
Example:
A grocery store observes how shoppers navigate aisles to decide where to place new products.
Advantages:
- Reveals real behavior (not just stated opinions)
- Ideal for UX and product design improvements
Disadvantages:
- Can’t reveal why users behave a certain way
- Ethical or privacy challenges, if not handled properly
5. Experiments and A/B Testing (Primary Research)
What it is:
Businesses use controlled tests to compare two versions of a marketing campaign, webpage, or product to see which performs better.
Example:
An e-commerce site tests two landing page designs to measure which one drives more sales.
Advantages:
- Data-driven decision-making
- Helps optimize marketing and product design
Disadvantages:
- Requires technical setup and enough traffic volume
- Limited to short-term behavioral outcomes
6. Secondary Data Analysis (Secondary Research)
What it is:
This involves using already-published data — such as government reports, academic research, or industry analyses — to draw insights without conducting new surveys.
Example:
A business consulting firm uses U.S. Census and Statista data to understand demographic trends before expanding into a new region.
Advantages:
- Affordable and fast
- Reliable if sources are credible
Disadvantages:
- Data might be outdated
- Not tailored to your specific business needs
7. Competitive Analysis (Secondary Research)
What it is:
Competitive analysis examines competitors’ products, marketing strategies, and market share to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
Example:
A clothing brand studies top competitors’ social media ads, pricing, and reviews to refine its strategy.
Advantages:
- Reveals gaps in the market
- Inspires new ideas and differentiators
Disadvantages:
- May rely on incomplete or public information
- Doesn’t capture hidden business strategies
8. Social Media Listening (Primary & Secondary Hybrid)
What it is:
Using tools like Hootsuite or Brandwatch, companies monitor conversations on social platforms to understand trends, sentiments, and brand perception.
Example:
A food brand tracks mentions of “healthy snacks” on X (Twitter) and TikTok to spot rising flavor trends.
Advantages:
- Real-time insights
- Great for brand reputation management
Disadvantages:
- Requires ongoing monitoring
- Sentiment data can be messy or misinterpreted
9. Market Segmentation Research
What it is:
Segmentation divides a broad target market into smaller, specific groups based on demographics, behavior, or psychographics.
Example:
A fitness app identifies segments like “busy professionals” and “students” to tailor messaging accordingly.
Advantages:
- Enables targeted marketing and personalization
- Improves ROI and customer satisfaction
Disadvantages:
- Requires quality data and analysis tools
- Over-segmentation may fragment resources
10. Trend and Predictive Analysis
What it is:
This advanced research method uses big data, AI, and analytics to predict future market movements, consumer behavior, and product demand.
Example:
A streaming platform uses predictive analytics to recommend new shows based on viewing patterns.
Advantages:
- Future-focused and strategic
- Increases accuracy in decision-making
Disadvantages:
- Requires technical expertise and data infrastructure
- Costly for smaller businesses
Key Tools and Software for Market Research
| Category | Tools | Best For |
| Survey Tools | SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Forms | Gathering direct feedback |
| Analytics Platforms | Tableau, Power BI, Google Analytics | Data visualization and trend analysis |
| Social Listening | Brandwatch, Hootsuite | Tracking brand sentiment |
| Data Sources | Statista, NielsenIQ, Pew Research | Market reports and consumer data |
Emerging Trends & The Future of Market Research
- AI & Predictive Analytics: Automated data interpretation and trend forecasting.
- Emotion Tracking: Facial recognition and neuro-marketing tools.
- Mobile-First Research: Surveys optimized for smartphone users.
- Real-Time Insights: Instant consumer feedback via social platforms.
The future of market research lies in combining human insight with AI precision — understanding not just what customers say, but what they truly mean.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using biased survey questions that skew results.
- Relying on a single data source.
- Ignoring small sample sizes in quantitative studies.
- Failing to interpret results into action.
Avoid these pitfalls by planning carefully, validating data, and staying objective.
Real-World Examples of Market Research in Action
- Starbucks – Uses customer surveys and app data to refine drink options.
- Nike – Leverages social listening to design trend-responsive campaigns.
- Amazon – Employs predictive analytics to recommend products and plan inventory.
These examples show how smart research turns data into competitive advantage.
FAQs About Market Research Methods
- What are the main types of market research methods?
Primary, secondary, qualitative, and quantitative. - Which method is best for startups?
Startups benefit most from surveys and focus groups to test new ideas quickly. - How much does market research cost?
It varies — online surveys can be low-cost, while in-depth studies may require a professional agency. - How is AI changing market research?
AI helps automate data analysis, uncover sentiment patterns, and predict future trends faster than manual methods. - What’s the biggest mistake in market research?
Ignoring what the data actually says and relying on assumptions instead of facts.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Market Research Methods
The best market research strategy blends data, empathy, and action.
By understanding both what customers do (quantitative) and why they do it (qualitative), businesses can create products, marketing, and experiences that truly resonate.
In 2025 and beyond, success belongs to those who listen, analyze, and adapt — using modern market research methods as their compass for smarter, evidence-based decisions.
Read Also:
- Renters Insurance: Protect Your Belongings and Peace of Mind
- Masari Cabal | The Financial Social Network Designed for Traders & Investors
- ImmoScout | 15 Powerful Facts You Can’t Afford to Miss
- 1262.76 of 4536.00 Is What Percent? | Calculate the Percentage
- How to Calculate YOY (Year Over Year) Growth for 3 Years (Step-by-Step Guide) 2025
- What Changes Are Coming to Social Security in 2025-2026?

